





Tierdermatologie Deisenhofen Consultations
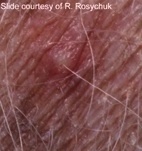
Papules may be present with or without pustules. Papules represent a
collection of inflammatory cells within the dermis and it is these cells which
result in the dermal swelling.
Some will be centred on a hair follicle => perifolliculitis is likely, so one must consider the follicular infections demodicosis, dermatophytosis and bacterial pyoderma.
Some papules will have the surface "excoriated" or - especially in the case of a spongiotic allergic reaction - will have formed a small vesicle on the top which rapidly ruptures. These are called crusted papules.
An interfollicular papule is frequently associated with insect bites (mosquito bite/ culicoides bite/ flea bite hypersensitivity).
Pustules are accumulations of cells and frequently serum within an intraepidermal space. Neutrophils and / or eosinophils give pustules their opaque colour. They are most frequently associated with infections and care should be taken (as in papules) to determine whether the pustule is centred on a hair follicle.
In the rare case of pemphigus foliaceus, the pustules may be large and contain numbers of - and groups of - acantholytic cells. It is important to remember that acantholytic cells may also be obtained from pyoderma pustules, a diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceus requires a skin biopsy!
Care should be taken when sampling a pustule for cytology. So that the cells in the underlying dermis are not also collected, hold the needle tip parallel to the surface of the skin.
Some will be centred on a hair follicle => perifolliculitis is likely, so one must consider the follicular infections demodicosis, dermatophytosis and bacterial pyoderma.
Some papules will have the surface "excoriated" or - especially in the case of a spongiotic allergic reaction - will have formed a small vesicle on the top which rapidly ruptures. These are called crusted papules.
An interfollicular papule is frequently associated with insect bites (mosquito bite/ culicoides bite/ flea bite hypersensitivity).
Pustules are accumulations of cells and frequently serum within an intraepidermal space. Neutrophils and / or eosinophils give pustules their opaque colour. They are most frequently associated with infections and care should be taken (as in papules) to determine whether the pustule is centred on a hair follicle.
In the rare case of pemphigus foliaceus, the pustules may be large and contain numbers of - and groups of - acantholytic cells. It is important to remember that acantholytic cells may also be obtained from pyoderma pustules, a diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceus requires a skin biopsy!
Care should be taken when sampling a pustule for cytology. So that the cells in the underlying dermis are not also collected, hold the needle tip parallel to the surface of the skin.
A follicular pustule
Impetiginous pustules
Papules and
haemorrhagic bullae











